

Health benefits of water-based exercise.2021 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. This section will focus predominantly on patients with an early chronic effusion of unknown etiology after TKA. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. knee pain in those with and without effusion, we randomly sampled 150 knees with varying degrees of effusion, oversampling the most informative knees with no or small effusions that had pain or no pain. A patient’s expectation after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is a knee that is painless and functional in terms of movement, strength, and endurance without signs of inflammation. Palpate for warmth, swelling (including bony swelling, effusion and bursal or other soft tissue swelling) and tenderness. We link primary sources - including studies, scientific references, and statistics - within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. Also known as a joint aspiration, the procedure involves taking the inside of the knee for analysis such as cell counts, culturing bacteria, and examining. hemarthrosis, or bleeding into the jointĮxcess weight and obesity may also increase the risk by placing strain on the knee.infections, such as Lyme disease or syphilis.overuse, due to certain physical activities or sports.
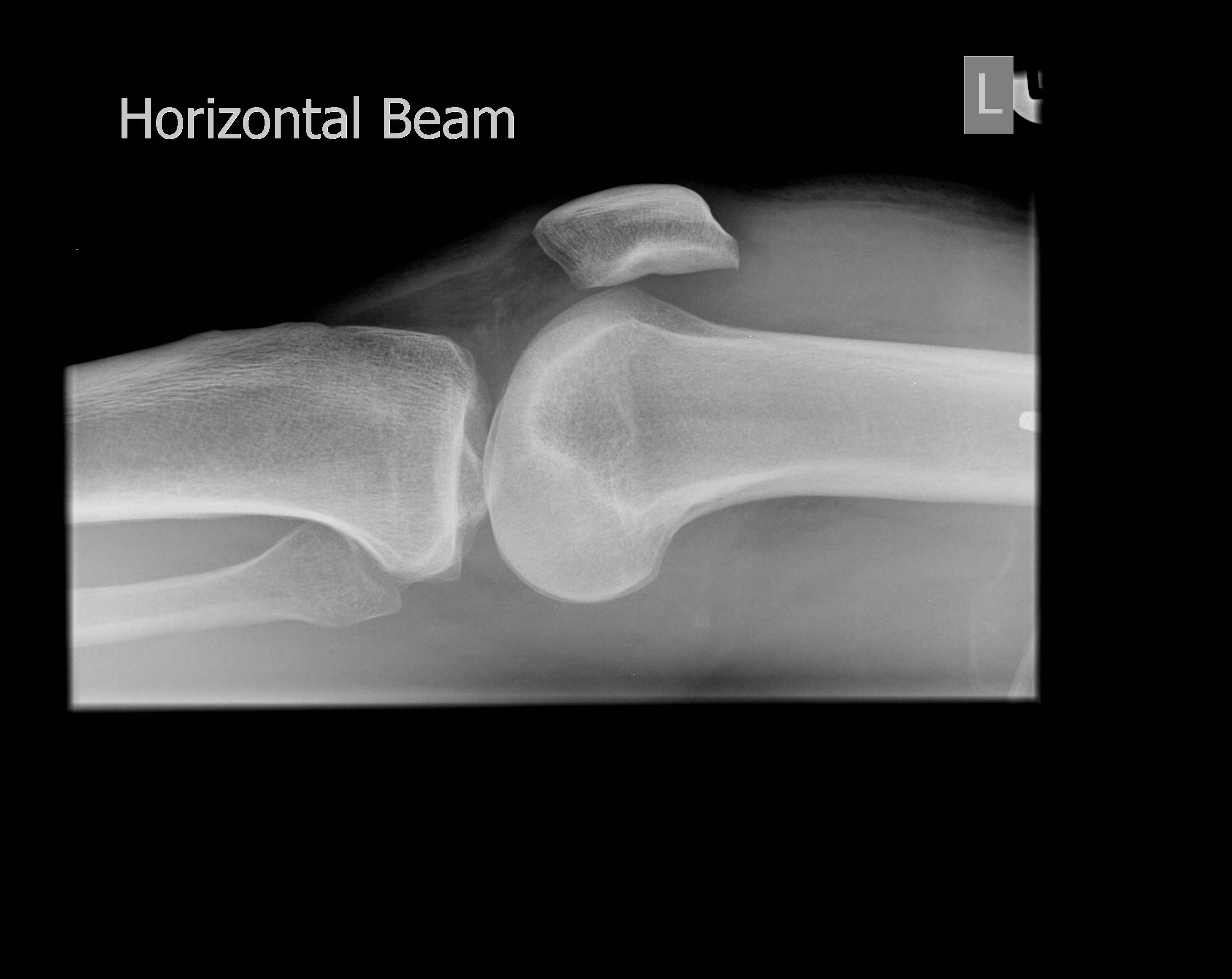
a traumatic injury, leading to a fracture or ligament damage.
#Knee effusion how to
Here's how to treat an effusion and when to see a doctor. Tests on fluid may show that one of the following has occurred or is present: Although visualization of articular fluid on MR images of the knee is common, no specific MR criteria that enable assessment of the quantity of the effusion. Excess fluid on the knee joint can lead to swelling and pain, a condition called an effusion. The results will show them what caused the problem and how to treat it. A doctor may remove some of the fluid and send it for testing in the lab. The type of fluid that accumulates around the knee depends on the underlying disease, condition, or type of traumatic injury that caused the excess fluid. Fluid on the knee can cause discomfort and is usually a sign that something is wrong. Inflammation and swelling can result from a traumatic injury, arthritis, or an infection. Share on Pinterest A traumatic knee effusion may feature puffiness or swelling of the joint and surrounding area.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
